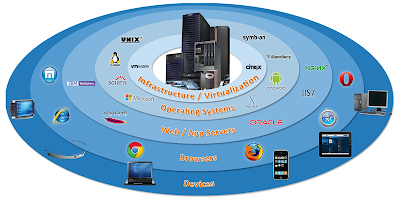
What is Compatibility Testing
- Compatibility testing is to check whether your software is capable of running on different hardware, operating systems, applications , network environments or mobile devices.
- Compatibility Testing is a type of the Non-functional testing
- Initial phase of compatibility testing is to define the set of environments or platforms the application is expected to work on.
- Tester should have enough knowledge on the platforms / software / hardware to understand the expected application behavior under different configurations.
- Environment needs to be set-up for testing with different platforms, devices, networks to check whether your application runs well under different configurations.
- Report the bugs .Fix the defects. Re-test to confirm defect fixing.
Types of Compatibility testing :
- Hardware
- Operating Systems
- Software
- Network
- Browser
- Devices
- Mobile
- Versions of the software
Let’s look into compatibility testing types briefly.
Hardware : It checks software to be compatible with different hardware configurations .
Operating Systems: It checks your software to be compatible with different Operating Systems like Windows , Unix , Mac OS etc.
Software: It checks your developed software to be compatible with other software’s.For example: MS Word application should be compatible with other softwares like MS Outlook,MS Excel , VBA etc.
Network: Evaluation of performance of system In network with varying parameters such as Bandwidth, Operating speed, Capacity. It also checks application in different networks with all parameters mentioned earlier.
Browser: It checks compatibility of your website with different browsers like Firefox , Google Chrome , Internet Explorer etc.
Devices : It checks compatibility of your software with different devices like USB port Devices, Printers and Scanners, Other media devices and Blue tooth.
Mobile: Checking you software is compatible with mobile platforms like Android , iOS etc.
Versions of the software: It is verifying you software application to be compatible with different versions of software.For instance checking your Microsoft Word to be compatible with Windows 7, Windows 7 SP1 , Windows 7 SP 2 , Windows 7 SP 3.
There are two types of version checking.
- Types of Version Checking
- Backward compatibility Testing
- Forward compatibility Testing
Backward compatibility Testing : is to verify the behavior of the developed hardware/software with the older versions of the hardware/software.
Forward compatibility Testing : is to verify the behavior of the developed hardware/software with the newer versions of the hardware/software.
Tools for compatibility testing
- Adobe Browser Lab – Browser Compatibility Testing - This tool helps check your application in different browsers.
- Secure Platform – Hardware Compatibility tool - This tools includes necessary drivers for a specific hardware platform and it provides information on tool to check for CD burning process with CD burning tools.
- Virtual Desktops - Operating System Compatibility - This is used to run the applications in multiple operating systems as virtual machines. N Number of systems can be connected and compare the results.